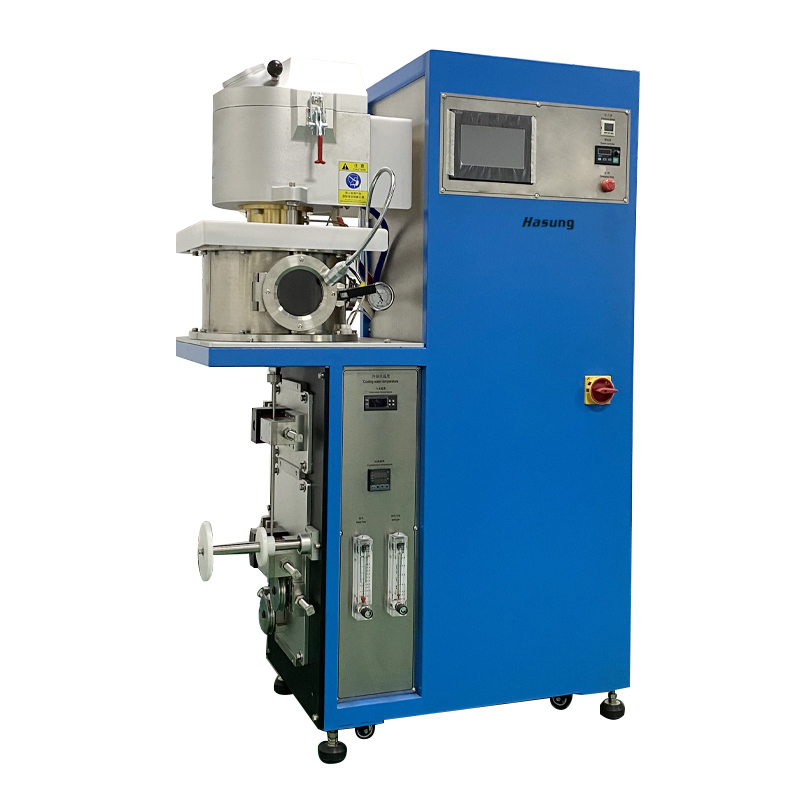
What Are Continuous Casting Machines?
Continuous casting machines (CCMs) are an essential component of the modern day metalworking industry, altering how metals are produced and molded. CCMs have significantly boosted production efficiency by enabling the smooth transfer of molten metal into semi-finished forms such as billets, rods, and slabs. Their ability to accelerate operations while upholding high quality has made them essential for a variety of applications in industry.
Understanding the Continuous Casting Process
The continuous process of casting is an accomplishment of engineering, turning molten metal into solid shapes in a simplified, unbroken flow. Despite typical batch processing that involves numerous separate processes, CCMs enable the smooth transition of liquid metal to formed structures.
The procedure starts with molten metal being poured into a mold, after which it cools and solidifies. The slightly solidified metal is constantly extracted, resulting in a steady production flow. With batch processing that requires individual heating, pouring, and cooling cycles, CCMs minimize downtime and provide unmatched efficiency. This ongoing technique is the cornerstone of contemporary metal manufacturing, ensuring accuracy, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
Key Components of Continuous Casting Machines
To accomplish the accuracy and effectiveness of continuous casting, CCMs utilize a collection of specific components that operate together:
1. Molten Metal Ladle: The ladle is used as a reservoir, supplying liquid metal to the casting procedure. The layout allows a regulated flow, eliminating splashing and providing an uninterrupted supply to the mold.
2. Mold: At the foundation of the process, a mold begins with the transformation of molten metal into a solid state. The outermost layers are frequently water-cooled to speed up solidification and ensure the metal keeps its form.
3. Cooling System: During the mold, the metal quickly cools down using sprays or baths. This step is critical to developing a homogeneous microstructure, and it has an immediate bearing on the overall quality of the finished product.
4. Withdrawal and Cutting Systems: As the metal becomes harder, it is continuously removed and cut to the required lengths. Superior cutting mechanisms offer clean, accurate edges, ready for the item for more processing.
Types of Continuous Casting Machines
CCM casting machines are accessible in two main versions, both customized for particular industrial applications:
✔Vertical Continuous Casting Machine
Vertical continuous casting machines are appropriate for generating high-purity metals and specialization alloys. Their vertical shape enables consistent cooling and decreases the risk of surface flaws, which makes them ideal for premium-grade goods that include copper and aluminum.

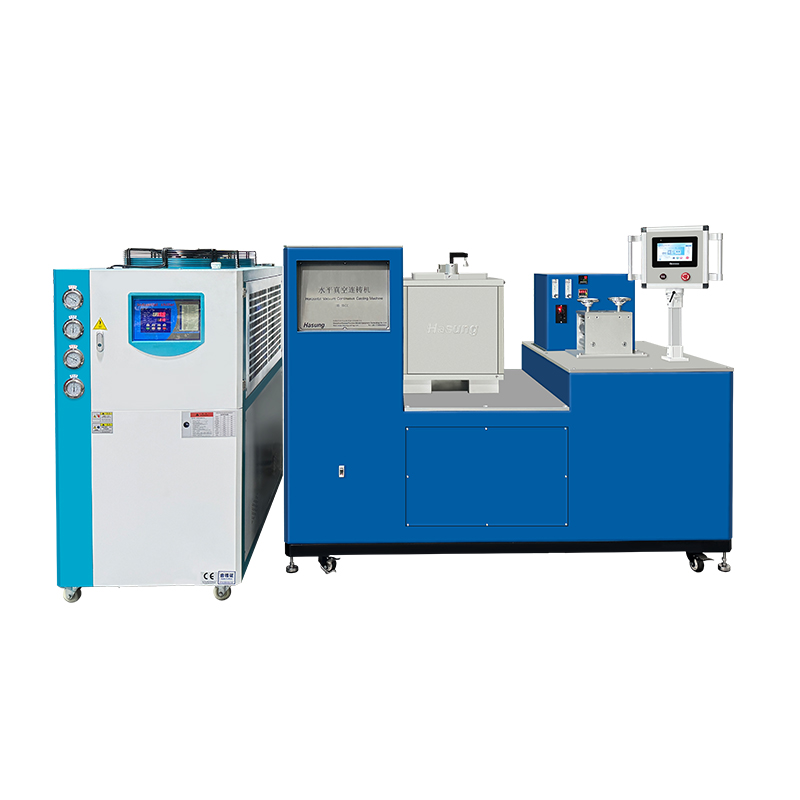
✔Horizontal Continuous Casting Machines
Horizontal continuous casting machines are typically employed for lengthy components like rods and tubes. Their inadequate shape makes them suitable for facilities that have restricted vertical space while nevertheless retaining great production efficiency.

Working Principle
To achieve the most favorable outcome that is possible, the continuous casting process is carefully regulated. Here's a simple breakdown:
● Molten Metal Feeding: Molten metal is brought into the mold through a regulated process, maintaining a smooth and uniform flow.
● Initial Solidification in the Mold: Provided the molten metal reaches the mold, the outer layer hardens, creating a shell that serves as a structural frame for future cooling.
● Secondary Cooling: When the semi-solid metal undergoes a number of cooling sprays, its center solidifies. Maintaining a suitable temperature is essential at this step to avoid challenges like fractures and inclusions.
● Inert Gas Application: For the prevention of oxidation throughout the entire process, an inert gas (such as argon) is introduced, culminating in a safe environment.
● Withdrawal & Cutting: The solidified metal is constantly eliminated and cut to the required lengths using automatic cutting devices, prepared to undergo additional processing or consumption.
Advantages of Continuous Casting Technology
Continuous casting procedure has numerous benefits, which makes it an increasingly common method in modern manufacturing:
▶ High Efficiency & Productivity: CCMs' flawless operation prevents downtime, enabling large-scale manufacturing with few interruptions.
▶ Superior Quality: Modern cooling systems & careful control guarantee that the products that are produced have low impurities and a uniform microstructure.
▶ Reduced Material Wastage: Despite older individuals' processes, CCMs reduce metals damage, rendering the process environmentally conscious and cost-effective.
▶ Scalability & Versatility: CCMs can deal with a variety of metals, notably steel, aluminum, copper, & their alloys, providing an extensive variety of business needs.
Applications of Continuous Casting Machines
Continuous casting furnace's versatility renders them important in a variety of industries.
● Metal Production
CCMs are frequently utilized in the manufacturing of steel, aluminum, & copper. They need to be produced for the manufacture of billets, slabs, and rods, a variety of raw materials used in the construction, automotive, & electrical sectors.
● Jewelry Manufacturing
These technologies create high-precision gold & silver wires used for excellent jewelry creation.
● Specialized Applications
CCMs manufacture particular alloys & high-purity metal including aerospace, medical, & electronics sectors.
Technological Advancements in CCMs
Continuous casting methodology changes, and such as advances to improve efficiency and quality:
■ Improved Mold Designs: Recent developments in mold technologies have enhanced heat transmission, leading to more uniform cooling & fewer surface flaws.
■ Automation & Monitoring Systems: Contemporary CCM continuous casting machine include continuous monitoring systems which identify deviations, assuring high standards while lowering manual involvement.
■ Eco-Friendly Designs: With an increasing concentration on ecological responsibility, CCMs are currently being constructed to be efficient in terms of energy lowering the carbon footprint of metal production.
Challenges and Solutions
Considering their apparent advantages, continuous casting furnaces deal with challenges.
◆ Surface Cracking: Nonuniform refrigeration can cause ruptures on the product's surface, jeopardizing its structural integrity.
◆ Solution: Modern cooling systems & precise temperature regulation have been designed to effectively address this problem.
◆ Non-Uniform Solidification: Differences in cooling rates may give rise to unequal solidification, leading in an uneven microstructure.
◆ Solution: The latest machines utilize highly sophisticated sensors that continually assess and alter cooling circumstances, maintaining consistency.

Conclusion
Continuous casting machines are an essential part in modern metalworking, providing efficiency, quality, & sustainability. The ability of these machines to convert molten metal into high-precision semi-finished goods has revolutionized sectors including construction to jewelry manufacturing.
As technological advances strengthen their capabilities, CCMs will continue to play an even greater role in environmentally friendly manufacturing, meeting the ever-increasing need for excellent metals. Their innovative designs and agility guarantee their ongoing relevance as they impact the future of metal manufacturing. Find detaisl about horizontal continuous casting machines and vertical continuous casting machine on Hasung!

Tel: +86 17898439424
E-mail: sales@hasungmachinery.com
WhatsApp: 0086 17898439424
Address: No.11, Jinyuan 1st Road, Heao Community, Yuanshan Street, Longgang District, ShenZhen, China 518115